Introduction
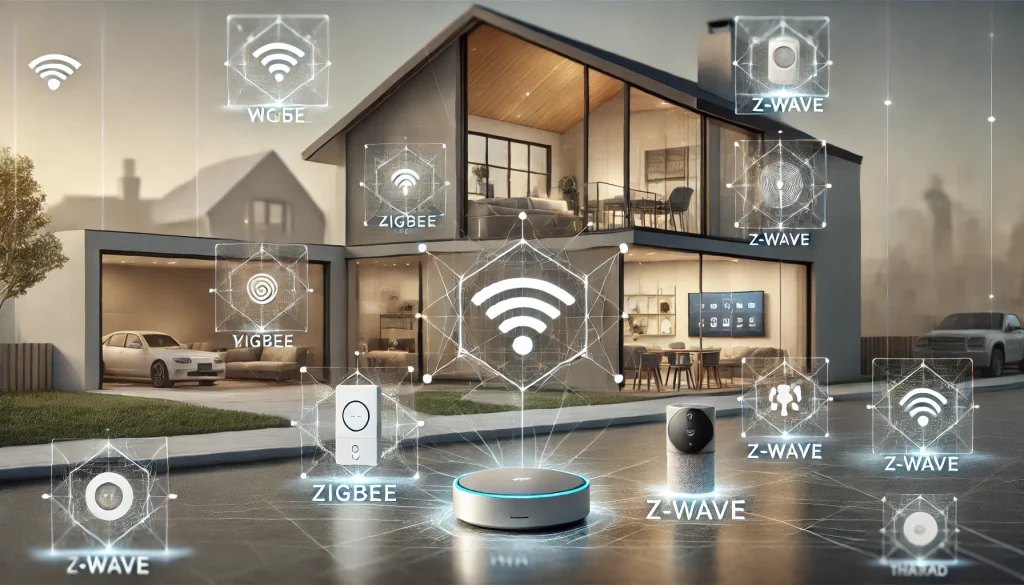
In the world of smart home technology, various wireless communication protocols connect devices and enable seamless automation. The most popular protocols are Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Z-Wave, Matter, and Thread. Each protocol has unique features and use cases. Let’s explore their differences to help you decide about your smart home setup.
Wi-Fi
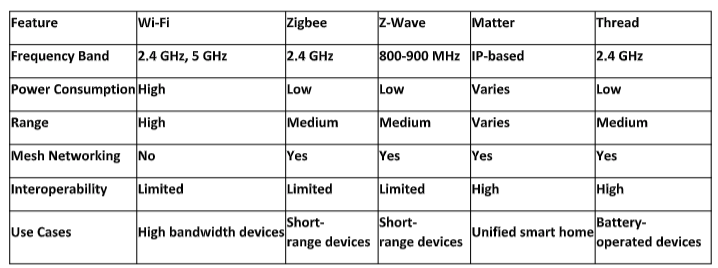
Wi-Fi is a widely used wireless communication technology that allows devices to connect to the Internet and communicate with each other wirelessly. It operates in the 2.4 and 5 GHz frequency bands and transmits high-speed data. Wi-Fi is ideal for devices that require large bandwidth, such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, and smart TVs. However, it consumes more power and may not be suitable for battery-operated devices.
Zigbee
Zigbee is a low-power, mesh network protocol that operates in the 2.4 GHz frequency band. It is designed for short-range communication and is commonly used in smart home devices like lights, sensors, and thermostats. Zigbee’s mesh networking capability allows devices to communicate with each other, extending the range and reliability of the network. It is known for its low power consumption and ability to support many devices.
Z-Wave
Z-Wave is another low-power, mesh network protocol that operates in the 800-900 MHz frequency band. It is widely used in smart home devices, especially for security, lighting, climate control, and access control. Z-Wave also supports mesh networking, allowing devices to act as repeaters and extend the network’s range. It is known for its reliability, scalability, and backward compatibility.
Matter
Matter is a unified standard developed by the Connectivity Standards Alliance (CSA) to create a secure and interoperable ecosystem for smart home devices. It is based on the Internet Protocol (IP), and existing technologies like Wi-Fi, Ethernet, or Thread can be used to connect devices. Matter aims to simplify the setup and management of smart home devices and ensure compatibility across different ecosystems. Matter supports many device types, including lights, locks, cameras, and thermostats.
Thread
Thread is a low-power, mesh network protocol that operates in the 2.4 GHz frequency band. It is designed for battery-operated devices and is known for its low power consumption and mesh networking capabilities. Thread allows devices to communicate with each other, extending the range and reliability of the network. It is often used in smart home devices like lights, locks, and sensors.
Conclusion
Each wireless communication protocol has strengths and weaknesses, and the choice depends on your specific needs and preferences. Wi-Fi is ideal for high-bandwidth devices, while Zigbee and Z-Wave are better suited for low-power, short-range devices. Matter and Thread offer enhanced interoperability and seamless connectivity for smart home devices.
Understanding the differences between these protocols can help you make an informed decision and create a smart home setup that meets your requirements.




